HashSetクラス・SortedSetクラスには集合演算を行うメソッドとして次のメソッドが用意されています。 いずれも引数としてIEnumerable<T>を取り、戻り値はありません(void)。 したがって、これらのメソッドでは引数に指定された配列やコレクションなどとの演算結果をインスタンス自身に反映します。
| メソッド | 動作 |
|---|---|
|
HashSet.IntersectWith
SortedSet.IntersectWith |
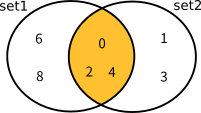
現在の集合と引数で指定されたIEnumerable<T>との積集合を求める (引数の集合と共通する要素のみを残す) |
|
HashSet.UnionWith
SortedSet.UnionWith |
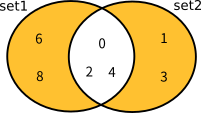
現在の集合と引数で指定されたIEnumerable<T>との和集合を求める (引数の集合の要素をマージする) |
|
HashSet.ExceptWith
SortedSet.ExceptWith |
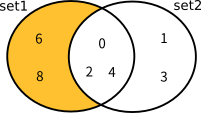
現在の集合と引数で指定されたIEnumerable<T>との差集合を求める (引数の集合の要素を除外する) |
|
HashSet.SymmetricExceptWith
SortedSet.SymmetricExceptWith |
現在の集合と引数で指定されたIEnumerable<T>との対称差を求める (引数の集合と共通する要素のみを除外する) |
以下は、上記の集合演算を使った例です。
SortedSetで積集合・和集合・差集合・対象差を求める
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Sample {
static void Main()
{
var set1 = new int[] {6, 2, 0, 4, 8};
var set2 = new int[] {3, 1, 2, 0, 4};
// 積集合を求める(IntersectWith)
var s1 = new SortedSet<int>(set1);
s1.IntersectWith(set2);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(", ", s1));
// 和集合を求める(UnionWith)
var s2 = new SortedSet<int>(set1);
s2.UnionWith(set2);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(", ", s2));
// 差集合を求める(ExceptWith)
var s3 = new SortedSet<int>(set1);
s3.ExceptWith(set2);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(", ", s3));
// 対象差を求める(SymmetricExceptWith)
var s4 = new SortedSet<int>(set1);
s4.SymmetricExceptWith(set2);
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(", ", s4));
}
}
実行結果
0, 2, 4 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 6, 8 1, 3, 6, 8
SortedSetで並べ替えが行われる以外は、結果は同じです。
以下の図は、上記のHashSet・SortedSetの集合演算メソッドの実行結果を図式化したものです。
IntersectWithの結果
UnionWithの結果
ExceptWithの結果
SymmetricExceptWithの結果